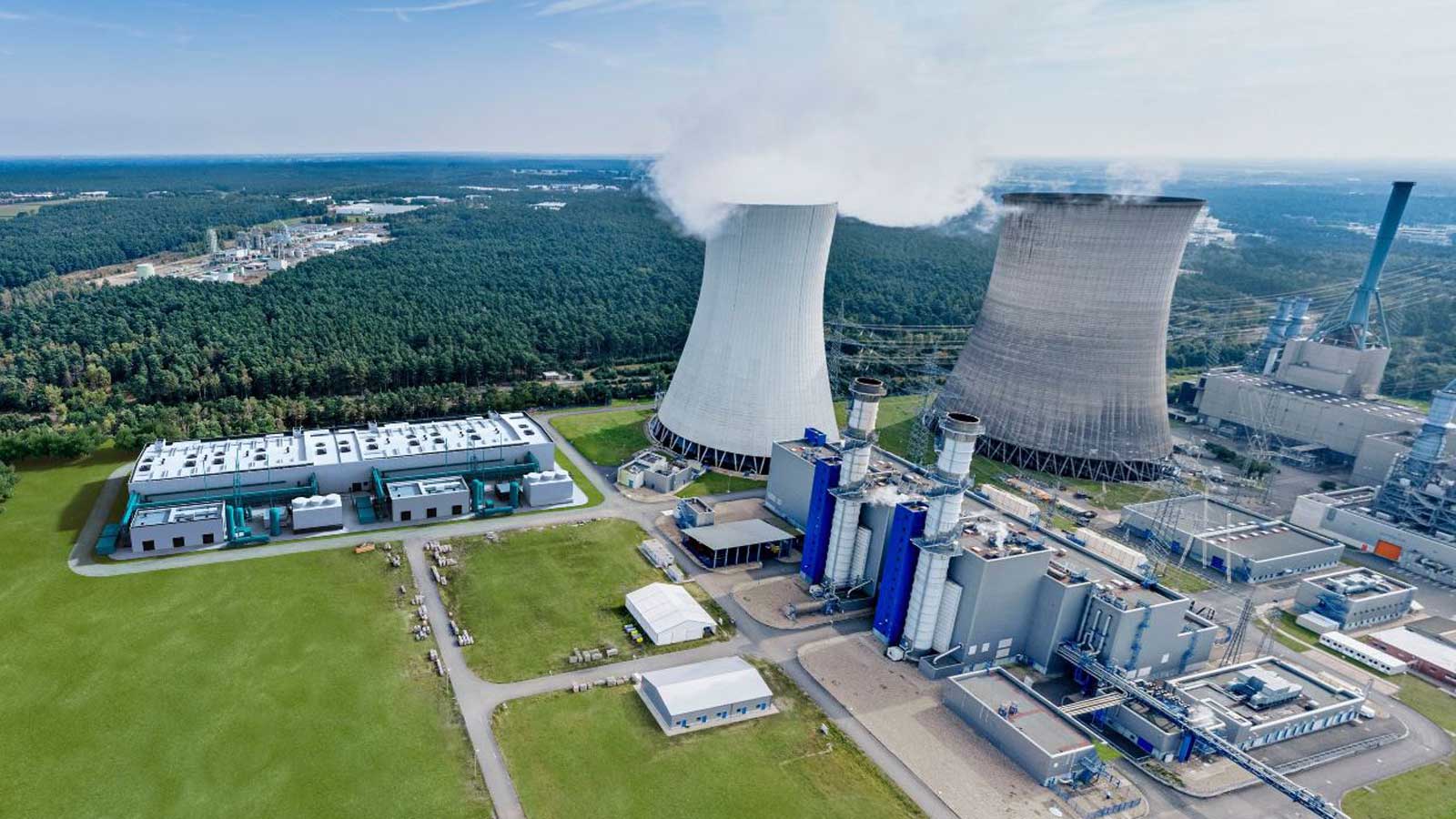
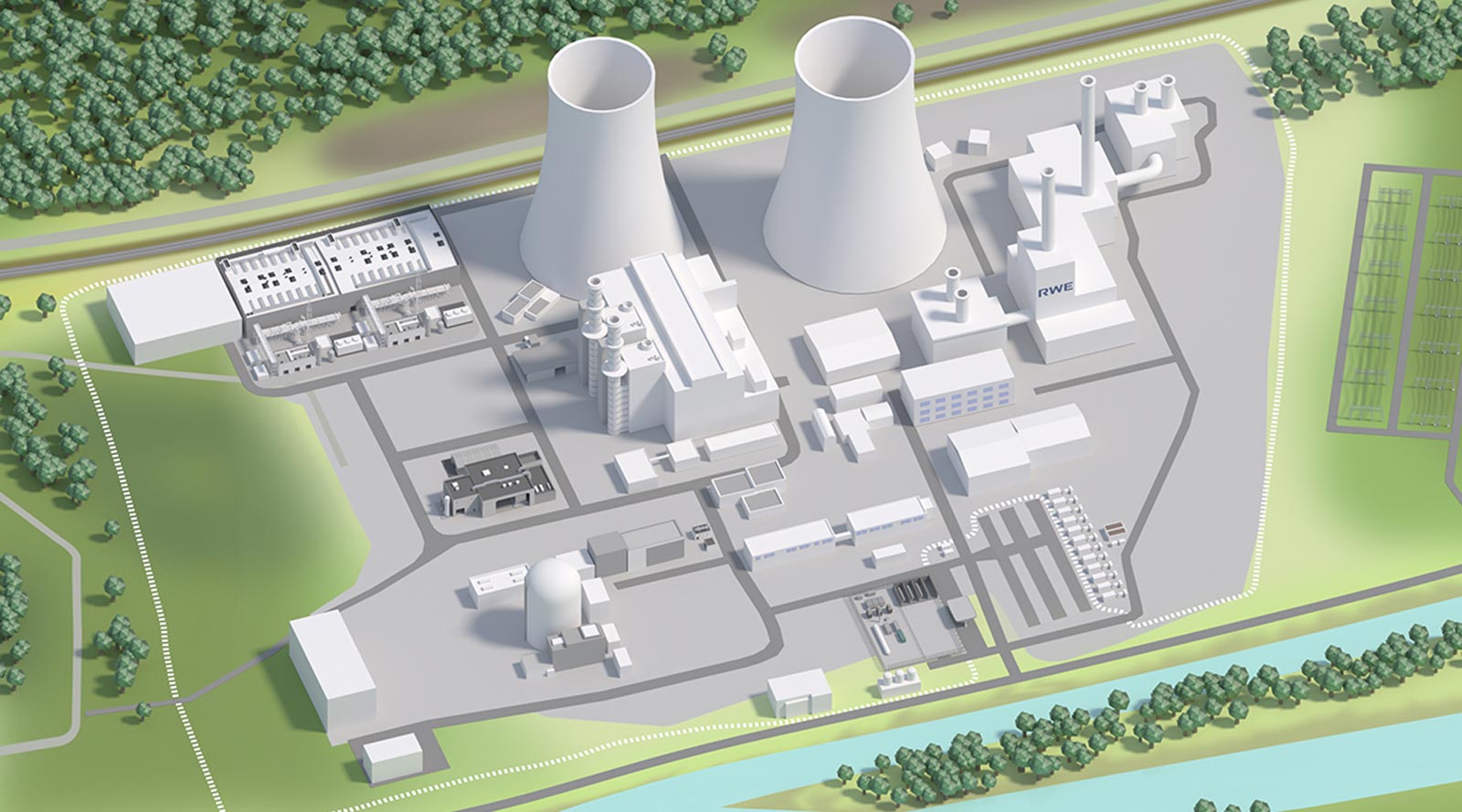
On this website you will find a digitally enhanced overview of the site with data and details on future-oriented projects. Give it a try! Use the following graphic to find information on completed facilities and planned projects.
Location Lingen
- H₂ pilot plant (14 MW)
- Hydrogen refuelling and filling station
- GET H₂ Nukleus (300 MW)
- Water treatment
- GET H₂ TransHyDE
- Megabattery 117+
- Direct reduction plant
- Unit D
- Cooling water pump house
- Hanekenfähr substation
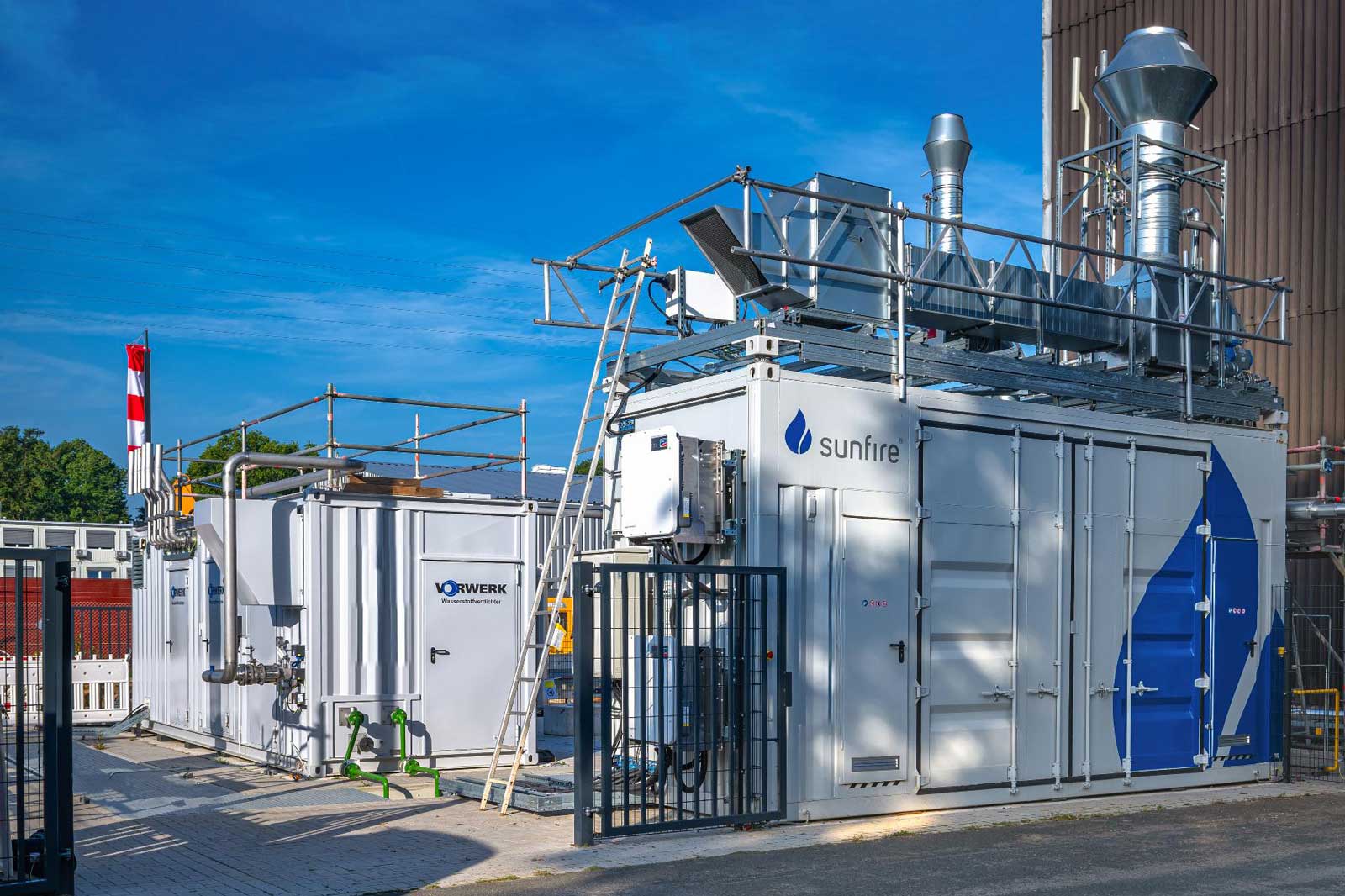
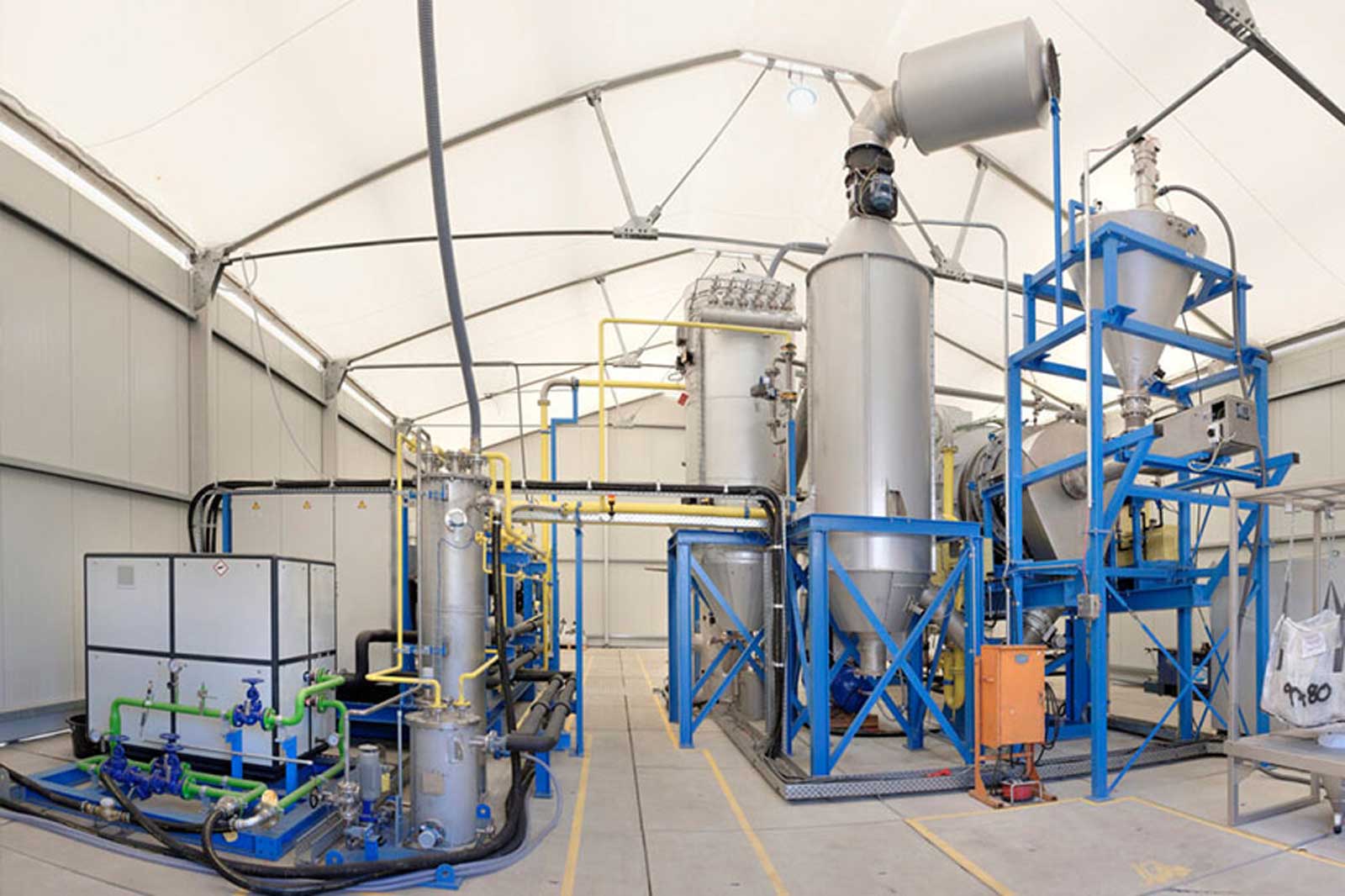
H₂ pilot plant (14 MW)
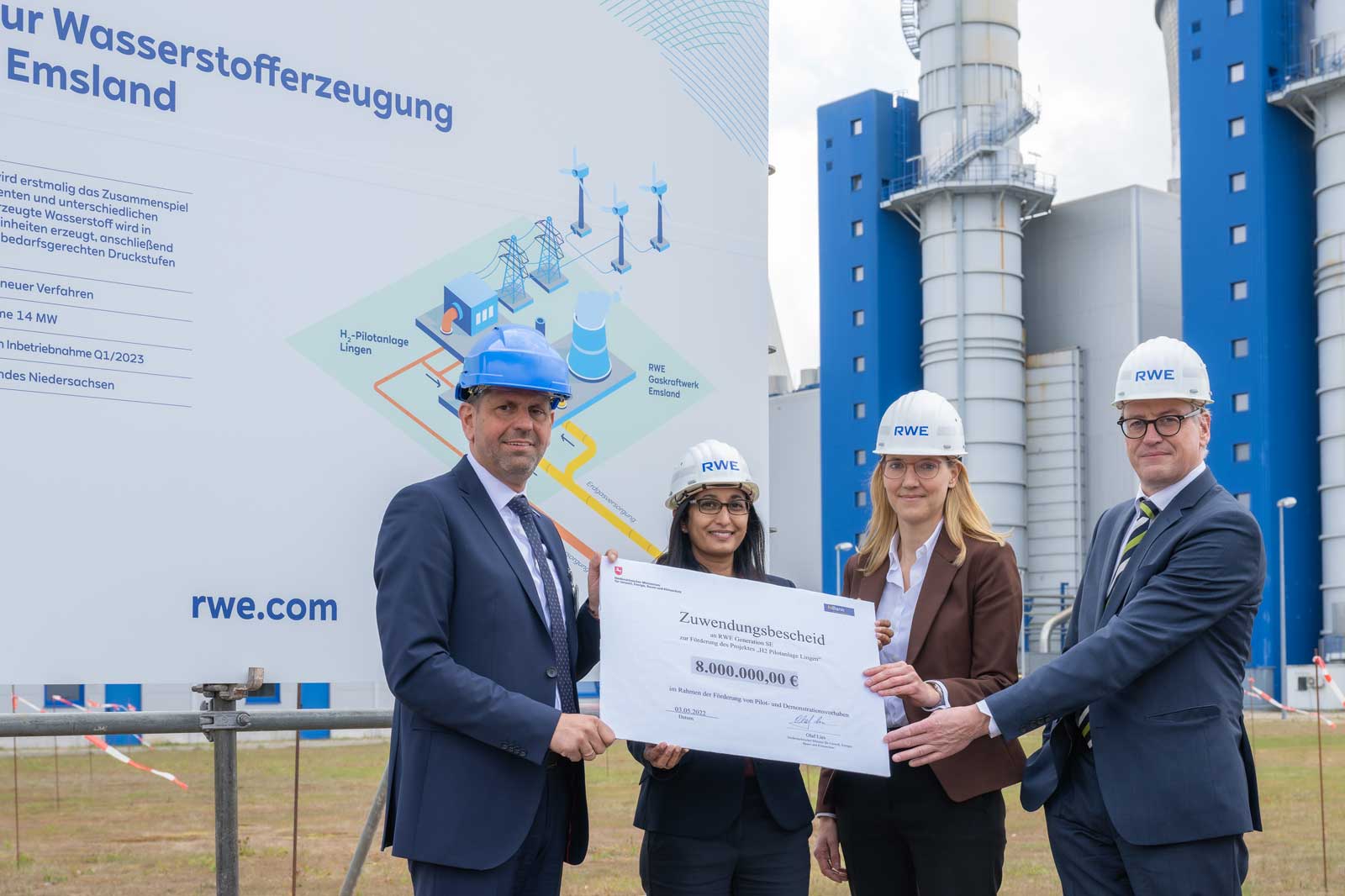
RWE operates a pilot electrolysis plant with a capacity of 14 megawatts (MW) as a test and pilot plant on the site of the Emsland gas-fired power station. As part of the project, two electrolysis technologies are being tested under industrial conditions and RWE is gaining insights on how the different components needed to generate hydrogen interact. This experience from the pilot plant can be used to optimise future operation of large-scale commercial facilities.
The plant comprises a 10-MW pressurised alkali electrolyser by Sunfire and a 4-MW PEM (proton exchange membrane) made by ITM. The plant uses electricity to generate up to 270 kilogrammes of hydrogen per hour.
The hydrogen from the pilot plant will initially be added to the fuel (natural gas) for the gas turbine of the RWE power plant. In the future, it will also be possible to feed it into the public hydrogen grid, which is currently being developed.
From mid-2025, hydrogen-powered vehicles can also be refuelled with hydrogen from the pilot at the Emsland gas-fired power plant. Companies that sign a purchase agreement with RWE will be able to retrieve green hydrogen from the pilot plant from 2025 using tank trailers and transport it to their operational sites.
Construction work on a hydrogen refuelling station and a filling station for the hydrogen has already begun.
In future, it will also be possible to feed the hydrogen into the public hydrogen grid, which is currently being developed.
The government of Lower Saxony has subsidised the pilot plant with 8 million euros. Construction work began in June 2022 and the first electrolysis modules arrived at the site in spring 2023.
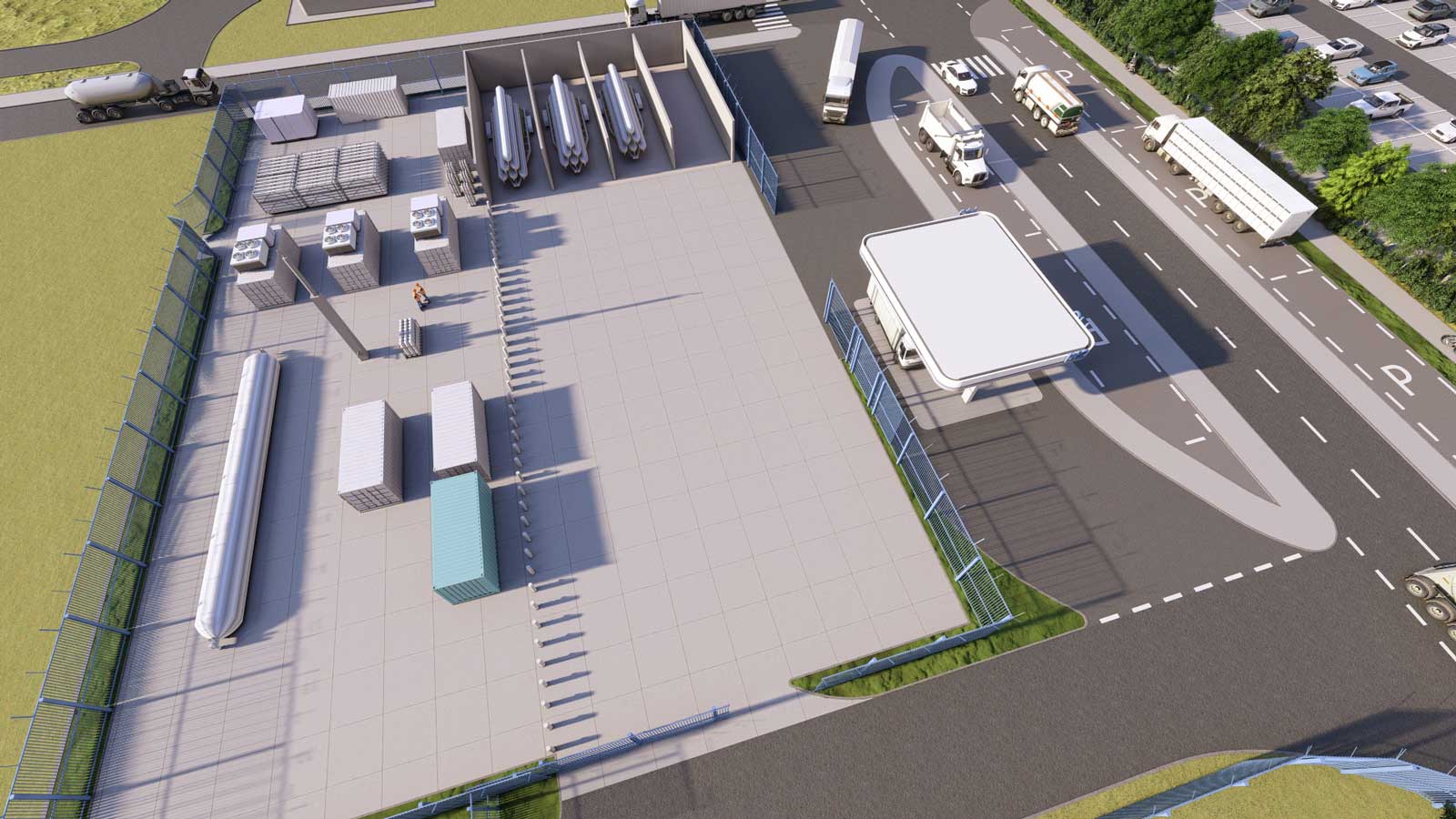
Hydrogen refuelling and filling station
RWE is building a trailer filling facility for green hydrogen and a public hydrogen filling station in collaboration with Westfalen Gruppe at the main entrance to the Emsland gas-fired power plant site. Lorries, buses, waste collection vehicles, vans and cars will be able to fill up with green hydrogen there. In addition, tanker lorries will be able to take on green hydrogen at the plant and distribute it to customers in the region. The facility will be operated by Westfalen Gruppe.
Construction work began in August. The filling station will enable companies that sign a purchase agreement with RWE to collect hydrogen with tank trailers and transport it to their sites from mid-2025.
The green hydrogen for the filling station and trailer filling plant will be generated at the 14-MW pilot electrolyser plant on the Emsland gas-fired power plant site, as well as other production plants.
The Lingen hydrogen refuelling station is being funded by the Federal Ministry for Digital and Transport Affairs with a total of over 6 million euros as part of the National Innovation Programme for Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technology. The funding programme is coordinated by NOW GmbH and implemented by Project Management Jülich (PtJ).
GET H₂ Nukleus (300 MW)
As part of the GET H2 Nukleus project, RWE is building an electrolysis plant with a capacity of 300 megawatts (MW) on the Emsland gas-fired power plant site by 2027. This will be realised in three expansion stages. The first 100 MW electrolysis plant is scheduled to be commissioned in 2025.
The project is aimed at generating green hydrogen for industrial customers at a commercial scale.
On 11 September, RWE announced that the companies Sunfire and Bilfinger have been commissioned with the construction of the third 100 MW construction line of the GET H2 Nukleus.
On 15 July 2024, RWE received a funding commitment from the federal and state governments for the implementation of the project. The federal government is providing 70 per cent of the funding. The state of Lower Saxony is contributing 30 per cent.
On 14 February 2024, the EU Commission granted the permission required under state aid law to support GET H2 Nukleus as part of an Important Project of Common European Interest (IPCEI). The project is now eligible to receive funding from the German government as well as state governments.
In 2022, the German government approved the early start of measures for GET H2 Nukleus. The reason for this early start is the requirement to adhere to the project schedule and the associated funding conditions. After approval was granted, RWE ordered the first two PEM electrolysers with a total capacity of 200 MW in December 2022.
In September 2023, the trade supervisory authority in Oldenburg granted permission for the construction and operation of the first two 100-MW electrolysers.
In 2021, the German government and the state government of Lower Saxony nominated GET H2 Nukleus to receive funding under the “Important Project of Common European Interest” (IPCEI) scheme.
Water treatment
Fully desalinated process and cooling water is required for generating hydrogen. RWE is constructing a new water treatment plant for processing and desalinating the water from the river Ems for the electrolyser plants. The water treatment plant is to be commissioned at the end of 2024.
GET H₂ TransHyDE
In September 2023, the first hydrogen was generated on the Emsland gas-fired power plant site – in a high-temperature, solid oxide cell electrolyser (SOEC) by Sunfire. The 0.25-MW facility is part of the GET H2 TransHyDE research project, which is investigating various aspects relating to the transport of hydrogen in the public gas supply system. The hydrogen is fed into a ring of pipelines consisting of new and existing lines at the site.
The GET H2 TransHyDE project looks into how hydrogen behaves in former natural gas pipelines and how its quality can be improved upon (recovery and purification). As part of the project, tests are carried out to see which materials are suitable for components of the hydrogen supply system. In addition, the project partners are optimising compressor designs and refining technologies for detecting leaks and inspecting and servicing pipelines.
RWE’s partners in the research project are Adlares GmbH, Evonik Operations GmbH, Meter-Q Solutions GmbH, Nowega GmbH, Open Grid Europe GmbH and Rosen Germany GmbH together with the DVGW Research Centre at the Engler-Bunte Institute of the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and the University of Potsdam.

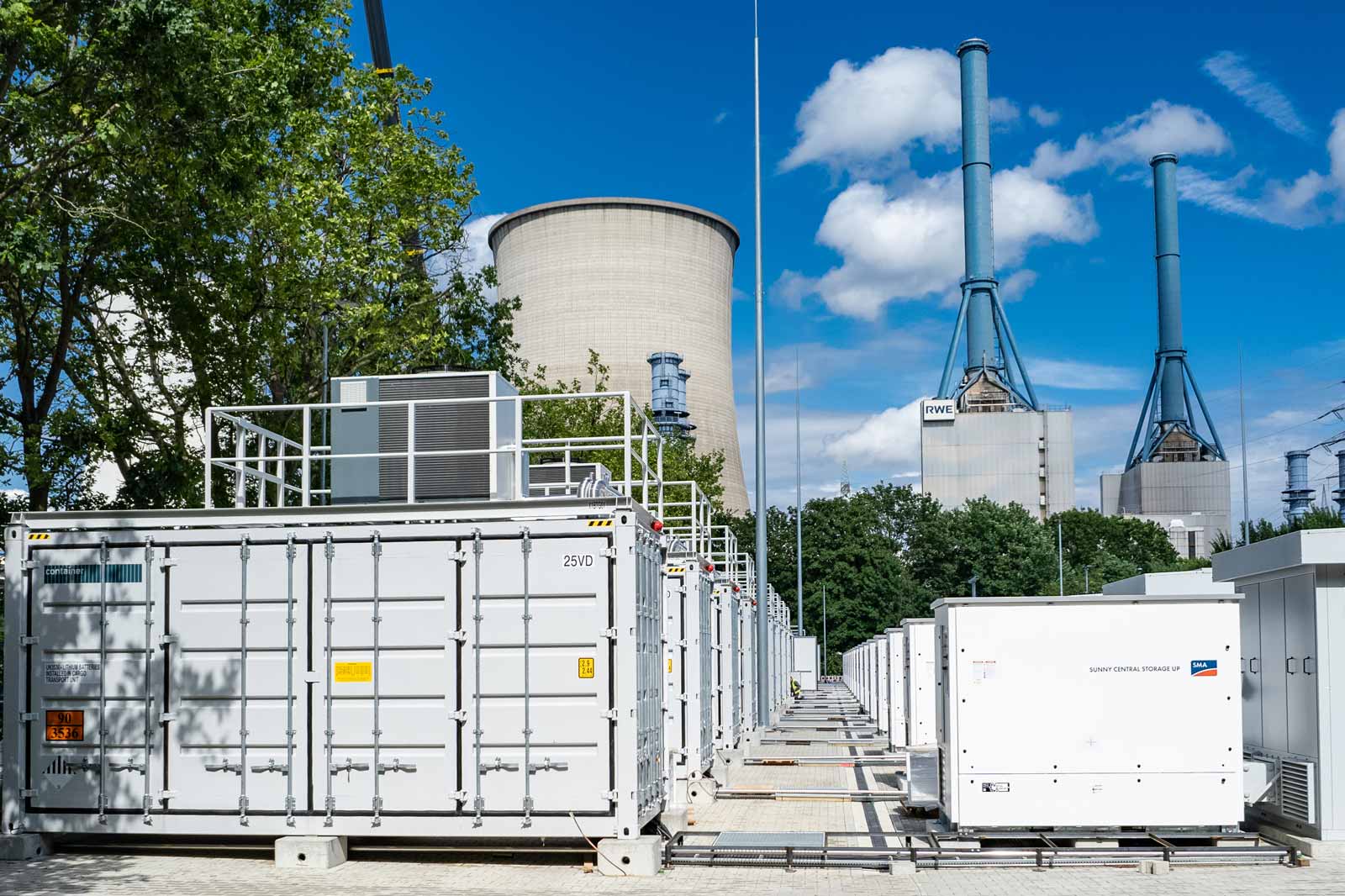
Megabattery 117+
The Emsland gas-fired power plant site is one of two locations of “Megabattery 117+”, one of the largest and most innovative battery storage systems in Germany.
RWE is deploying the Megabattery 117+ commercially in wholesale markets and in balancing energy markets. It is used to help balance short-term fluctuations on the electricity grid and is thus contributing towards integrating renewables into the energy system.
Its lithium-ion batteries are virtually linked to RWE’s run-of-river power plants on the river Moselle. During periods of electricity oversupply in the grid, the batteries store the electricity and, at the same time, the run-of-river power plants on the river Moselle reduce electricity production. In the opposite case of an electricity shortage in the grid, the batteries feed the stored electricity into the grid and the run-of-river power plants on the Moselle increase their electricity production.
By increasing or reducing the flow rate at the linked run-of-river power plants, RWE can provide additional capacity as balancing energy.
RWE has invested a total of approximately 50 million euros in the Megabattery in Lingen and Werne. The system has been operational since January 2023.
Direct reduction plant
Since August 2023, the HyIron group of companies has been operating a hydrogen-based direct reduction plant for producing green iron (DRI – direct reduced iron) on the site of RWE’s Emsland gas-fired power plant.
At the pilot plant, the system integration of DRI plants as consumers into the public hydrogen infrastructure is being tested.
The plant can produce iron from ore in a climate-neutral process using green hydrogen. The green hydrogen for the DRI plant is generated in RWE’s neighbouring electrolyser pilot plant.
The green raw iron from the DRI plant is then processed further in the Lingen steel plant by Benteler.

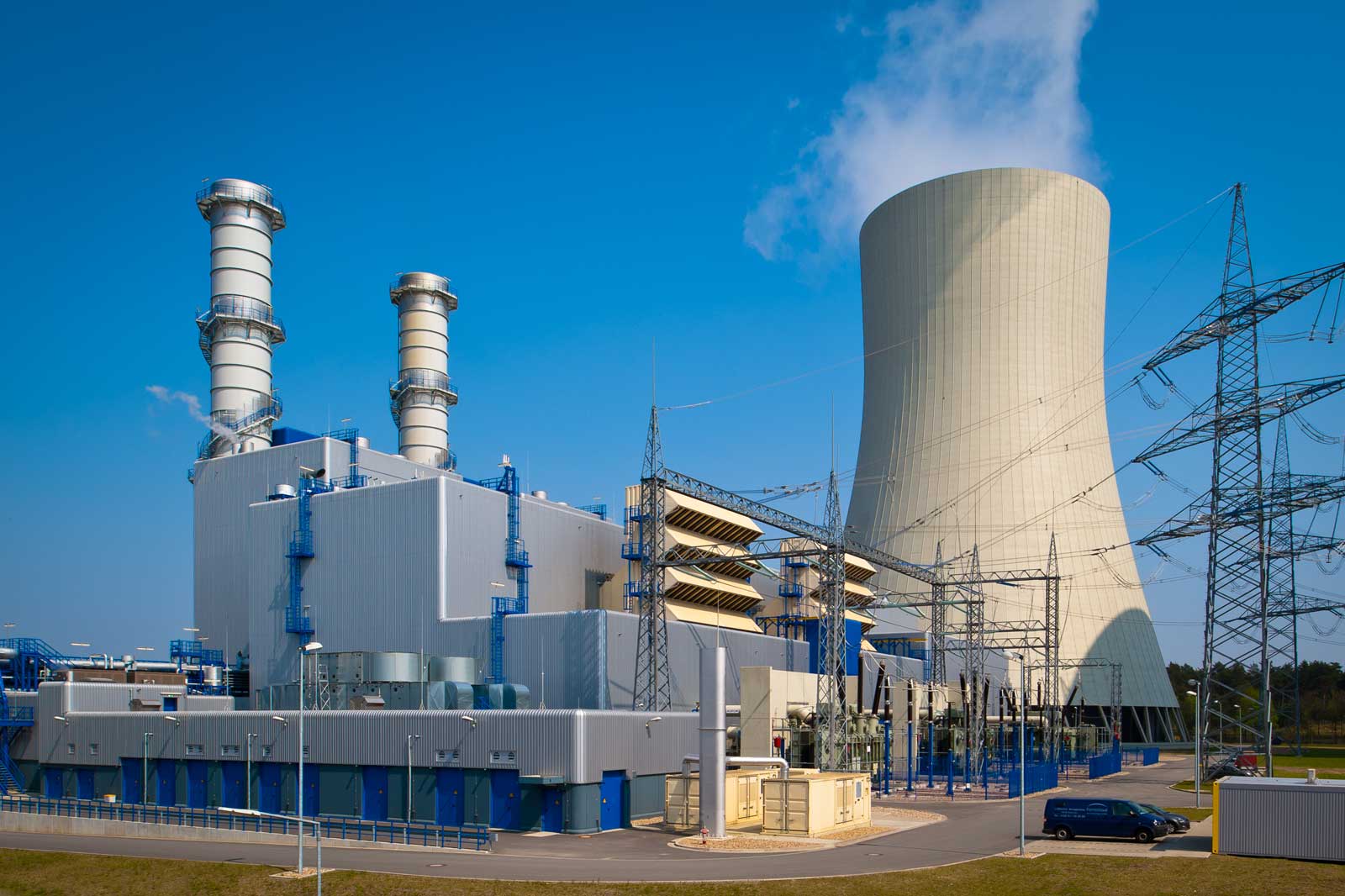
Unit D
Unit D of the gas and steam turbine power plant (CCGT plant) features two gas turbines with a total output of approximately 565 megawatts (MW) as well as two waste heat recovery boilers and a shared steam turbine with a capacity of 330 MW. The unit D CCGT has thus a total capacity of approximately 895 MW.
The 14-MW pilot electrolyser is connected to unit D via pipelines. Some of the hydrogen produced in the pilot plant will be added to the natural gas for the gas turbine in the future. It will be possible to mix up to 5% of hydrogen into the gas.
In this way RWE is gaining insights into using hydrogen in electricity generation.
Unit D was commissioned in 2010 and modernised in 2020 to further increase efficiency.

Cooling water pump house
RWE takes water from the river Ems via its cooling water pump house at Dortmund-Ems Canal. The river water is used to cool the plants (power plant and electrolysers) and as a base material (process water) for generating hydrogen.
Depending on its use, the water is pumped from the cooling water pump house to the water treatment plant where it is demineralised (desalinated) and then fed into the electrolysis process.
Hanekenfähr substation
In order to produce green hydrogen at the Emsland gas-fired power plant site, electricity generated from renewable sources is required there. To this end, electricity produced at wind farms in the North Sea is transported to Lingen, where it is transformed to the required voltage level in the Hanekenfähr substation and then distributed. The electricity coming from Hanekenfähr substation is then used to supply the electrolyser plants for producing hydrogen as well as other systems.
RWE in the Emsland region stands for 50 years of energy and innovation
Lingen is now RWE’s hydrogen showcase location
Lingen in Lower Saxony’s Emsland region is rapidly gaining importance for RWE and the European energy transition. Until recently the energy location was known mostly for the Emsland gas-fired power plant as well as the Emsland nuclear power station, which was taken offline in April 2023. Now Lingen has become Germany’s showcase location for hydrogen. There are few sites in Germany with a comparable density of hydrogen production and application, and soon also hydrogen-based electricity generation.
Perfect conditions for the green hydrogen economy
In Lingen, RWE can draw on its experience in developing and operating energy facilities to help in establishing hydrogen along the entire value chain. The company benefits from the perfect conditions at the site, which is connected to both the public gas grid and the public electricity grid. The river Ems ensures a reliable supply of water to all processes and plants. This is also the reason that one of Germany’s first 100% hydrogen-ready gas turbines and a hydrogen filling plant with filling station will soon operate alongside industrial scale electrolysers. As partners in the renewables sector, these plants will help industry and the mobility sector to achieve their climate targets. RWE is also using pilot plants to gain experience in operating various hydrogen technologies.

Lingen power stations visitor centre
Hydrogen
Send e-mail
Buying hydrogen
Best advices and smart business solutions for your company: Our team of experts is happy to advise you.
Contact us











